The Department of Materials Technology of the Institute of Technical Service employs qualified specialists in the field of materials science, engineering technology, metal forming. In addition to the educational process at the department following the specialization of teachers researched these areas.
Thus, at the Department of Materials Technology there is a laboratory of polymeric materials. Polymer filter elements developed in the laboratory have a unique set of physical and mechanical, electrical, thermal, chemical properties, high frost resistance and exceptional inertness to aggressive environments, satisfactory filtration, and hydraulic characteristics, the ability to regenerate repeatedly.

Polymer filter elements
Technological processes for the manufacture of polymer filter elements that provide a fineness of filtration of 40, 20, 10, 5, 3, 1 μm have been developed. Experimental and industrial batches of filter elements were made and used:
– in filters of water and oil separators (used in the automotive industry, in enterprises for the production of medicines, in breweries, distilleries, and factories for the production of soft drinks);
– in filters for purification of compressed oxygen (used at the enterprises of a military-industrial complex and in the medical industry);
– in filters for purification of carbon dioxide (in the production of soft drinks, where it is necessary to purify carbon dioxide from moisture and mechanical impurities);
– in separator filters (used in the gas industry for purification of natural gas from condensate, formation water and mechanical impurities);
– in the coal industry for the purification of mine gas, which is used as fuel in gas turbine and gas piston plants for electricity and heat;
– in fuel filters (used for fine cleaning of fuel in cars and trucks);
– in oil filters (used in hydraulic drives of machines, including CNC, to replace regular imported filters that have exhausted the resource);
– in oil filters in power and mechanical engineering for purification of the transformer, turbine, and industrial oils.
Annually, the department performs several research calculations with enterprises of various industries, which developed technological processes for the manufacture of polymer filter elements that provide a fineness of filtration of 40, 20, 10, 5, 3, 1 μm, as well as developed technical conditions for “Elements filtering from fluoroplastic 4”.
In the manufacture of porous material it is necessary to take into account that the resulting material must have high permeability and be strong enough. Therefore, when creating a porous material, it is necessary to choose the optimal porosity in combination with the dispersion of the pore former that meets these requirements. In this regard, an original program of graphic computer modeling of the pore structure of materials has been developed.
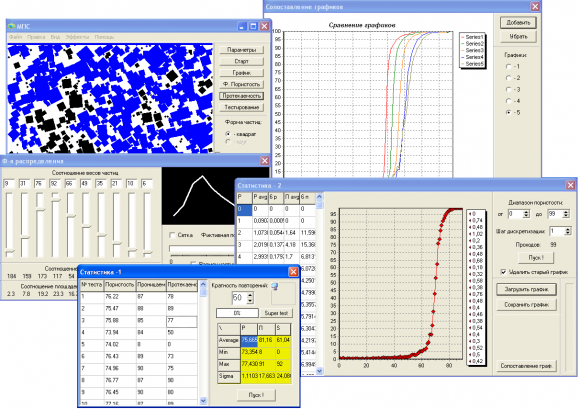
Graphic computer modeling program pore structure of materials
The latest developments of the laboratory are filter elements made of fluoroplastic-4 designed for purification of gases and liquids, as well as for the separation of water and oils from compressed gases. The separator of separation of water-fuel emulsion with a productivity of 60 l / min which provides efficiency of water separation not less is developed and madeη = 98 % .


Installation for cleaning and dehydration of diesel fuel
In the field of metal processing by pressure at the department researches of technology of deformation strengthening of bent rolled profiles for agricultural mechanical engineering by a method of roll forming are carried out..
The technology of deformation strengthening of flat sites of high-quality, sheet and special bent profiles of hire is developed.
The essence of the technology is to apply on certain areas of the sheet blank, corresponding to the flat elements of the finished profile, groups of longitudinal corrugations of sinusoidal or semicircular shape in height, a height comparable to the thickness of the molded profile. The application of such corrugations takes place by the method of roll forming due to the local extraction of the metal of the workpiece in a pair of reinforced rolls having a calibration corresponding to the applied corrugations.
The rolls that form the corrugation are located at the beginning of the profile-bending state. With the subsequent shaping of the profile to the desired configuration in the subsequent state stands in the calibers of the forming stands provide appropriate releases to skip the previously formed corrugations. The offered technology allows us to receive bent profiles of any con obtained by this technology showed that the yield strength, which is usually carried out strength calculations of metal structures, such profiles increase to 22 – 25%, the yield strength to 7-9%.
figuration up to 2,5 mm thick with the strengthening corrugations put on flat elements.
Due to riveting at cold plastic deformation there is a possibility of receiving stronger profiles with the most rational distribution of metal on the section. The field tests of the profiles
Besides, the deformation strengthening of the walls of the profile in addition to increasing the strength characteristics in the areas of corrugation formation leads to their alignment in the cross-section of the profile as a whole, which has a positive effect on the bearing capacity of the profile.
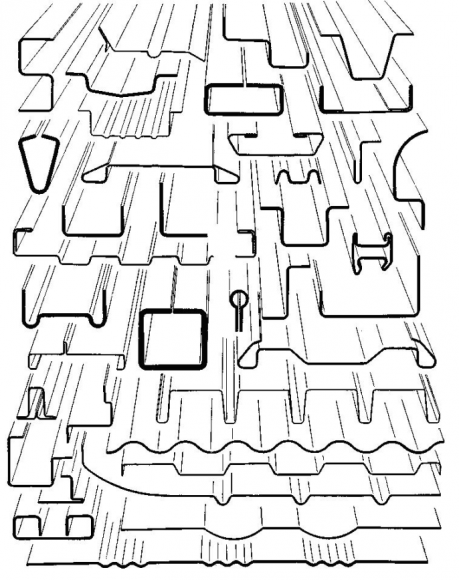
А)
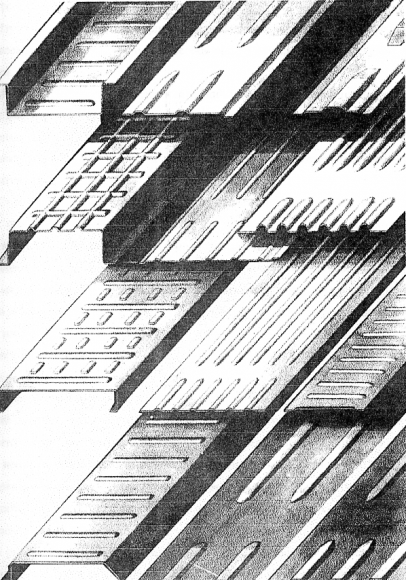
Б)
Assortment of bent profiles (A) and high rigidity profiles (B) mastered in the industry,


Gondola car with upper and lower cladding of high rigidity profiles
Research work in the field of plastic deformation of metals, improvement, and scientific substantiation of theoretical and technological aspects of manufacturing one of the most important for the machine-building complex type of effective metal products – bent profiles with special service properties. According to the results of the performed researches, for the first time in the world practice, a specialized unit 1-5×300-1650 was created, put into operation at the Magnitogorsk Metallurgical Plant. The assortment mastered with his participation in the unit consists of more than 100 highly efficient high-rigidity profiles, which are supplied to machine-building enterprises of various industries. The total volume of production of profiles on the unit exceeds 3.5 million tons, and their use in the construction of modern machines and structures has saved more than 80 thousand tons of metal. Scientific developments of Trishevsky OI repeatedly demonstrated at exhibitions of achievements of the national economy of the USSR and Ukraine and awarded the Diploma of the 1st degree, gold, silver, and two bronze medals.
As part of the development of new innovative technologies, the last two years have paid special attention to the possibility of increasing the operational stability of thin-walled cutting tools for food processing industries. In particular, a set of works was performed for the Kharkivyanka confectionery factory. The beginning of the research was to study the initial state of the material and the damageability of the tool. It is established that the reason for the failure of knives is the fragile destruction of working surfaces, deformation of the cutting blade, its blunting due to the destruction of the carbide phase, carbon diffusion, and plastic deformation, as well as fatigue failure of the middle part of the knife. Based on the performed theoretical and experimental researches, new complex technological processes of strengthening of knives by nanocoatings are offered. At the same time, design solutions with the formation of stiffening strips were introduced to provide resistance to fatigue failure of knives.

Disc knife spindle assembly with stiffness strips
Different components of coatings and the optimal thickness of the applied layer were used. Reinforcement was applied from only one surface of the knife, which ensured its self-sharpening during operation. The possibilities of overheating of thin-walled products during hardening were taken into account. At the same time achieved an increase in hardness and strength of the knives. The tendency to corrosion was reduced by pre-RF treatment of the surface of the cutting tool. The developed complex technology provided an increase of durability, reliability, and safety of users of the tool (possibility of destruction at operation with a hit of metal in processing products is excluded). The quality of disc knives in the manufacture, hardening, and operation was evaluated by specially developed new methods of optical – mathematical processing of metallographic images and non – destructive testing.
The result of fruitful work is the introduction of scientific developments and proposed technologies in the industry at PJSC “Confectionery Factory” Kharkivyanka “with an economic effect of 51.11 thousand UAH. per year (when strengthened by nanocoating WС with a thickness of 100 nm) and 61 thousand UAH. per year (CrN 900 nm coating).

Installation of the CD-A model for crushing nuts
The new complex strengthening technology is planned to be introduced in the future at the enterprises of the processing industry. The expected economic effect of the expansion of implementation will be 183 thousand UAH. when using reinforced disc knives at three enterprises of the industry within their annual needs. The developed technologies can also be used to increase the stability of the cutting tool installed on various equipment of the American company “Urschel Laboratories Incorporated”, which is used in many enterprises of the food industry of Ukraine to cut a wide range of products such as vegetables, fruits, including citrus peels, frozen meat, and roots. It can be effective to strengthen the cutting tool, which is installed on equipment for packaging material, processing of cocoa beans, sugar beets, and tobacco.
The results of developments are published in 36 scientific papers and are protected by 6 patents, which fully cover the essence of the research.
The department also conducts work related to the development of new progressive areas of research on the structure and properties of metal alloys through non-destructive testing.
Thus, one of these areas is research aimed at improving the manufacturability of products from high-alloy iron-carbon alloys, including high-chromium cast iron, by reducing the share of residual austenite in the structure of such alloys. The solution to this problem was achieved based on studying the peculiarities of the transformation of residual austenite during casting and heat treatment to ensure its maximum decomposition and stabilization of the properties of the material during operation. In solving this problem, a new effective composition of high-chromium cast iron was developed and the technology of optimal heat treatment in the temperature range of magnetic conversion of special carbides was proposed, which led to the complete decomposition of residual austenite. The proposed developments are protected by the Patents of Ukraine. The efficiency of the performed developments is confirmed by the metallurgical enterprises of Ukraine and is achieved by improving the quality, operational stability without increasing capital costs. For example, the introduction of results in the manufacture of rolled rolls made it possible to reduce downtime on transshipments by 8-10%, increase the operational stability of rolls by 1.5 times, reduce their costs, improve the quality of metal by 5-8%.
Employees of the department have developed and implemented new methods of mathematical processing of metallographic images that allow determining with high accuracy, including the structural components of high-alloy metal alloys with high inhomogeneity.
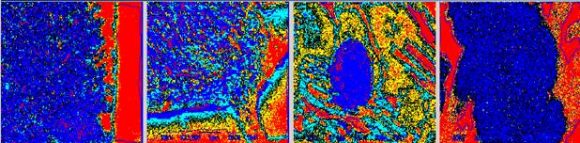
Histograms of phase distribution obtained as a result of mathematical processing of metallographic photographs of microstructures of high-chromium cast iron
With the help of these developments, studies of the dislocation structure, diffusion processes occurring during crystallization and heat treatment of materials, as well as to predict the structure and determine the properties that will be obtained under the proposed modes of heat treatment of materials.
Shortly the department plans to perform a set of research works on the theoretical and experimental substantiation of new effective processes to increase the operational stability of high carbon steel products by strengthening heat treatment.

